請看下面在最後, 留在或離開非洲遷徙人類的現代人類後代圖片。
Please see below at the end, the pictures of modern descendants of early humans stayed in or out of Africa.
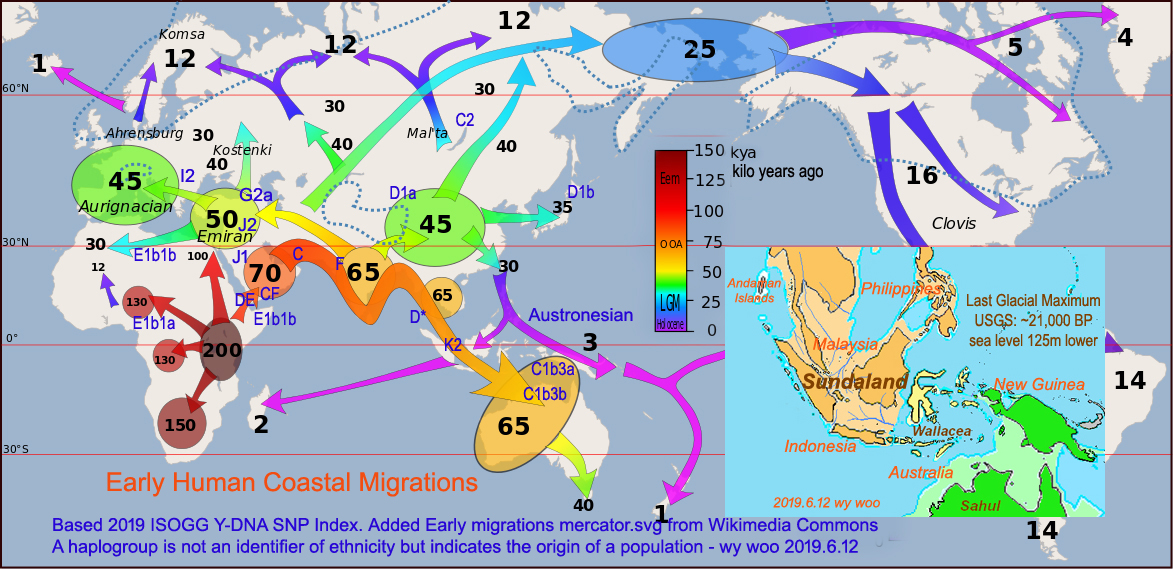
(Written 2019.6) Original Title: 早期人類沿海遷徙 Early Human Coastal Migrations:
在過去的幾年裡,基因檢測的進步改變了我們對早期歷史和文明的看法, 也改變了我們在旅行時了解當地人和文化的方式。使用單倍群不是政治和種族性的,因為它不是種族的標記,而是指出人類的起源。 現在英文維基百科,都有加這些資料。 In the past few years, the advance of genetic testing changes the way we look at early history and civilization. This is also change the ways we understand local people and culture when traveling. Using haplogroup is not political and racial related because it is not an identifier of ethnicity but indicates the origin of a population.
下面地圖顯示現代人的單倍群CF和DE,他們是M168的後代,部分大約7萬年前離開了非洲。
CF離開後再也沒有回來了, 然而DE分裂成D和E,E留在非洲成為Negroid大黑人(E1b1a),其中班圖人佔據了大部分撒哈拉以南地區,成為非洲最大的族群(76%)。 另一族群(E1b1b)被視為高加索種, 佔據了北非和非洲之角(17%)。Below map shows modern humans of haplogroups CF and DE, who were M168's offsprings, left Africa about 70,000 years ago. CF left and never returned. Then DE splitted into D and E. E stayed in Africa to become Negroid (E1b1a) in which Bantu occuppied most sub-Sahara and became the biggest group in Africa (76%). Another group (E1b1b), considered as Caucasiod, occuppied North and Horn of Africa (17%).
DE分裂後,據相信D先進入亞洲大陸,成為第一個現代人類定居東亞大陸者。他們成了羌族,白馬族和藏族等。 後來去了東南亞成為Negritos小黑人, 然後到了日本成為阿伊努人。 D-人群僅佔世界人口的2%。 請看下面現代人圖片, 顯示他們的多樣性。 After DE split, it is believed D went to mainland Asia first and became first human settlers in east Asia mainland.They became Qiang, Baima (means white horse) and Tibetans etc. After they went southeast Asia to become Negritos (means little blacks), and to Japan to become Ainu people. D-people only occupy 2% of world population. Please see below modern human pictures showing their diversity.
人類走出非洲(Out of Africa): CT-M168→DE,CF→C,F→G,HIJK→H,IJK→IJK→IJ,K→LT,K2→K2a(→NO),K2b(→MS,P→Q,R)
Note: 幾年前我在Previous Posts寫: "在7萬多年前人類走出非洲,其中D和E型的人群可能是在六、七萬年前紅海附近分離。攜帶E型的人回到非洲,成為非洲西部的Negroid大黑人;而攜帶D型的人輾轉向東遷徙,成為東南亞的Negrito小黑人"。 最近有人認為, 走出非洲不是七萬年前的M168的時候,DE和E並沒有走出, 而是更晚的6万年之內,C D F三支分別走出。
我們在摩洛哥旅行之後, 我發現E1b1b = Hamites(含族)不是黑人。
我們在巴爾幹半島和希臘旅行之後, 我發現希臘大陸人起源更接近北非E1b1b,而Create島人則來自西亞J2。
大約3600年前,猛烈火山爆發摧毀了希臘的Santorini島,留下了幾百米厚的火山灰。 Akrotiri鎮像Pompeii一樣被埋葬,為現代考古學家保留了許多精美的壁畫和藝術品。 請看史前人類和住宅視頻。
中國官方2018公佈"中華文明探源工程"成果, 距今約5,000年前,良著文化最早進入文明社會, 距今3,800年, 中華文明在自身發展過程中,廣泛吸收了外來文明的影響。源自西亞,中亞等地區的小麥栽培技術,黃牛和綿羊等家畜的飼養以及青銅冶煉技術逐步融入中華文明之中。
The new Y-DNA Haplogroup Trees 單倍群樹 (2022-2-14 Wikipedia) below show haplogroups A,B,E stayed in and haplogroups C,D,F out of Africa. Map notations new classification: D1a1a-M15, D1a1b-P99, D1a2a-M55, D1a2b-Y34637

上面地圖 Map Notations: (Written 2019.6)
C1b3a (formerly C2-M38): Indonesia, New Guinea, Melanesia, Micronesia, Polynesia
C1b3b (formerly C4-M347): Indigenous Australians
C2 (formerly C3-M217): Mongols, Kazakhs, Tungusic, Paleosiberians, Na-Dene
D* (M174): Negritos of Andaman Islands & Southesat Asia
D1a1 (formerly D1-M15): Qiang (羌族), Tibetan,
D1a2 (formerly D3-P99): Baima (白馬族), Pumi (普米族),
D1b (formerly D2-M55): Ainu, Yamato Japanese, Ryukyuan (Okinawa)
E1b1a (V38): Sub-Sahara, Negroid - Niger Congo (Bantu, Hutu, Tutsi, 76% of Africa)
E1b1b (M215): North Africa, Horn of Africa, Hamites (含族, Berber, Cushitic, Nilotic-Maasai, , 17% of Africa)
K2: Ancestor of most Asians, Europeans and Americans, 60% of world population
I2: Early Europeans (Balkans, Sardinia) before LGM (Last Glacial Maximum)
J1 (M267): Arabian Peninsula, Sudan, Ethiopia, West Asia, North Africa, Semites (閃族, Arabs & Jews etc.)
J2 (M172): Ancient Near East, Italy, Mediterranean littoral, Central Asia, South Asia
G2a (P15): Caucasia, Sardinia, Central & Southern Italy, Neolithic farmers & herders 6-9 kya. Ötzi the Iceman G2a2a2 (L91) 5 kya
Notable large expansions and migrations in early history:
Indo-European migrations 6 kya from Eurasian Pontic-Caspian steppe
Astronesin migrations 5 kya from Taiwan
Bantu expansions 4 kya from Western Africa
Arab conquests 7th century from Arabian Peninsula
Below pictures show the modern descendants of haplogroups A,B,C,D,E without F which constitutes most paternal lineages outside of Africa. Some pictures were taken by me and others were downloaded from internet. The picks were based upon the ethnic aspects of the humans. Fig (1): Modern descendants of Haplogroups C,D stayed out of Africa 單倍群C,D離開非洲的現代人類後代:

Fig (2): Modern descendants of Haplogroups A,B,E stayed in Africa 單倍群A,B,E留在非洲的現代人類後代:

吳偉榮2019夏 - revived 2022冬春


